THCA vs Delta 9
Cannabinoids have become increasingly popular in recent years as more states legalize cannabis and hemp-derived products. Two cannabinoids garnering significant interest are tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta 9 THC). Understanding the key differences between these plant compounds is important for consumers exploring the expanding legal cannabinoid marketplace. This article explores THCA and Delta 9 in detail, focusing on their special qualities and uses.


Key Takeaways
- THCA is the raw, non-psychoactive precursor to THC found in cannabis plants. On its own, it does not cause a high.
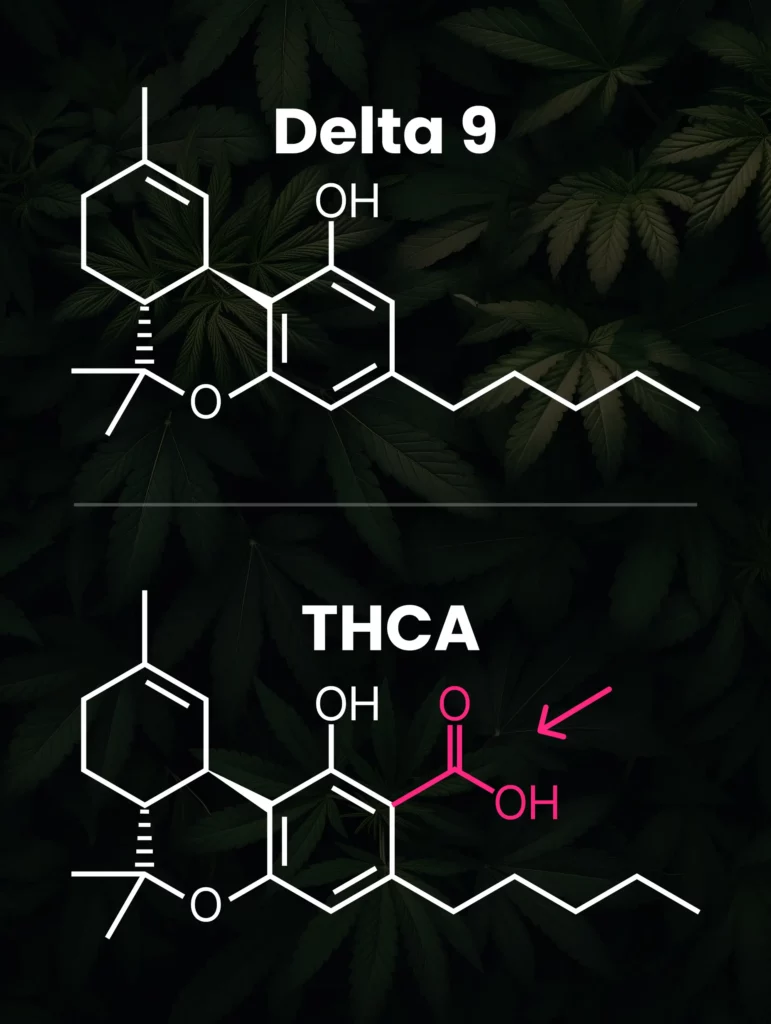
- When THCA goes through decarboxylation (removing a COOH group), it transforms into delta 9 THC which induces psychoactive effects by binding to CB1 receptors.
- Both THCA and delta 9 THC show therapeutic potential, but more clinical research is needed to confirm effects and safety.
- Delta 9 THC remains federally illegal, while hemp-derived THC under 0.3% d9 THC is federally legal legal. However, state laws vary.
What is THCA?

THCA is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found abundantly in raw, unheated cannabis plants. Its scientific name is tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, reflecting its acidic form. THCA is actually the precursor to the more famous THC before it undergoes decarboxylation when exposed to heat. In its raw form, THCA does not produce the intoxicating effects associated with THC.
Cannabinoids like THC and CBD are made naturally in cannabis plants. THCA is the first one produced through enzymes from CBGA. Heating cannabis converts THCA into THC through decarboxylation, which removes the acidic carboxyl group and activates it.
What is Delta 9 THC?

Delta 9 THC is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis responsible for its characteristic high. Its full name is delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Delta 9 THC activates the endocannabinoid system by attaching to CB1 receptors in the brain, causing feelings of happiness and relaxation.
THC is prohibited in the United States. Yet, Delta 9 THC derived from hemp containing less than 0.3% THC is permissible. This is sanctioned under the 2018 Agricultural Act. Delta 9 THC, when obtained from cannabis, continues to be a regulated substance under federal legislation.
Key Differences Between THCA and Delta 9
Now that we have the basics down, where exactly do THCA and delta 9 THC differ? They may sound almost identical, but there are some very important distinctions:
Chemical Structure
The main structural difference is that THCA contains an extra carboxyl group (COOH) which delta 9 THC lacks. This gives THCA a larger molecular size and different shape. It also makes THCA more unstable.
Psychoactive Effects
This difference in structure has huge implications on the effects of these cannabinoids:
- Delta 9 THC induces the classic cannabis high by binding to CB1 receptors in the brain.
- THCA alone does not cause psychoactive altered perception effects and will not make you high in its raw form.
- However, when THCA is decarboxylated into delta 9 THC through heating, then it takes on the intoxicating qualities of delta 9.
The Decarboxylation Process
Process called decarboxylation is when a carboxyl group is removed from a molecule – in this case, converting THCA into delta 9 THC. This reaction occurs with heat through:
- Smoking/vaping cannabis (temperatures over 200°C or 392°F)
- Heating cannabis in an oven (temperatures around 105°C or 221°F)
- Slow decarboxylation at room temperature over time
Once this happens, THCA becomes delta 9 THC and induces all the same effects. But in its raw form, THCA itself is non-psychoactive.
Potential Applications and Research
Scientific understanding of cannabis compounds is still evolving. Early research indicates both THCA and delta 9 THC may offer therapeutic potential.
THCA Research
Studies on THCA suggest it may have qualities like:
- Anti-inflammatory effects
- Neuroprotective properties to protect the brain
- Antinausea effects
Since it does not cause a high, THCA may be desirable for those seeking therapeutic potential benefits without psychoactivity. However, more studies are still needed.
Delta 9 THC Research
Studies on delta 9 thc on the other hand have explored its potential to help conditions like:
- Muscle spasticity in multiple sclerosis
- Poor appetite and weight loss
- Nausea during chemotherapy
- Anxiety (low doses)
Although promising, there are still unanswered questions around delta 9 THC’s long-term effects and medication interactions.
Legal Implications
Cannabis research has historically been limited by legal restrictions. The 2018 Farm Bill opened doors for hemp and marijuana – derived cannabinoid research. But delta 9 THC and marijuana remain federally illegal, slowing clinical research. Understanding the laws in your own state is important when accessing these compounds.
How to Consume THCA and Delta 9 Legally
If you choose to use either THCA or delta 9 THC, there are some consumption guidelines to follow based on federal and state laws:
THCA Consumption
- In raw, unheated form as capsules, tinctures, or juicing raw cannabis leaves
- Ensure any THCA cannabis products are sourced from legal hemp plants
- Avoid smoking or vaping THCA to prevent decarboxylation into delta 9 THC
Delta 9 THC Consumption
- Find out if recreational or medical marijuana is legal in your state
- Look for hemp-derived delta 9 THC products under the 0.3% limit
- Use vapes, tinctures, edibles or other products according to your state’s regulations
- Start low and slow with dosage; delta 9 THC is very potent
Consuming cannabinoids legally comes down to understanding your state laws and only accessing regulated, tested products that align with the regulations.
Final thoughts
THCA and Delta 9 THC are two popular cannabinoids from the cannabis plant gaining a lot of interest lately. THCA is found in raw, unheated cannabis. It’s non-psychoactive and doesn’t cause a high on its own. When THCA is heated, it loses a carboxyl group in a process called decarboxylation and gets converted into Delta 9 THC. This Delta 9 compound is responsible for the classic marijuana high feeling when it binds to receptors in the brain.
Some key differences between THCA and Delta 9 are that THCA has an extra carboxyl group chemically. THCA does not cause a high but can offer potential therapeutic benefits in its raw form, while heated Delta 9 induces psychoactive effects. Research is still limited but early studies show both compounds may help certain conditions. To use them properly, THCA should be consumed raw and unheated, while Delta 9 products need to comply with state cannabis laws. Understanding the distinct qualities of these two similar sounding cannabinoids will help consumers make informed choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between smoking THCA vs eating it?
Smoking or vaping THCA will cause decarboxylation and convert the THCA into delta 9 THC. This will result in psychoactive effects of delta. Eating raw THCA will not cause decarboxylation, so you can receive non-psychoactive benefits.
Is it permissible to travel with thca products?
The situation is not consistent. Items that contain THCA extracted from legal hemp with less than 0.3% delta 9 THC can typically be shipped domestically, but it’s essential to verify the rules of your target location. Full-spectrum THCA items might encounter additional limitations.
What's stronger, THCA diamonds or delta 9 vape carts?
THCA crystals or diamonds contain very concentrated levels of THCA. When vaporized, this potent THCA converts into very strong delta 9 THC side effects. Delta 9 vape carts provide the effects of pre-decarboxylated THC, so their strength depends on the concentration. Highly concentrated delta 9 oils can be very potent.
The statements on this blog are not intended to diagnose, cure, treat or prevent any disease. FDA has not evaluated statements contained within the blog. Information on this website or in any materials or communications from Inheal is for educational/informational purposes only and is not a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Please consult your healthcare provider before making any healthcare decisions, correct dosage or for guidance about a specific medical condition.

A connoisseur of cannabis creativity and true contemplation with more than 20 years of experience, Chris extracts deep thoughts from getting lightly baked and shares his wandering mind. He blends cuisine and cannabis culture into nutritious, delicious recipes and insights for other hemp lovers.
Related Posts

Delta 8 vs Delta 9: Which One Truly Reigns Supreme?

Comparing HHC vs Delta 8: Which is Right for Me? – Inheal

THCA Workout: Boost Athletic Performance with Raw Cannabis

THCA and Creativity: Inspiring Artists Musicians and Writers

Does THCA Show Up on a Drug Test?

Is THCA Legal in USA? State by State Guide

Uncovering the Secrets of THCA

Exploring Terpene Profiles of Popular THCA Strains

The Fine Art of Making THC-A Diamonds from Rosin
All Posts